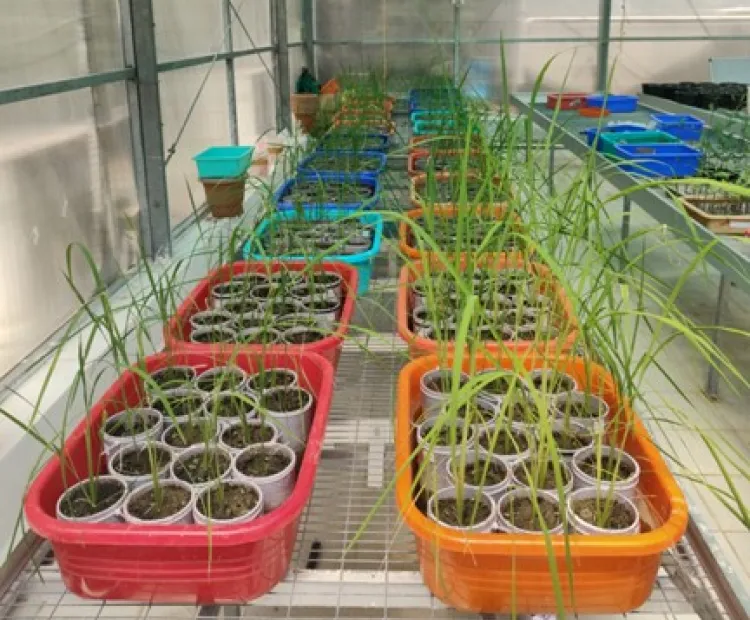
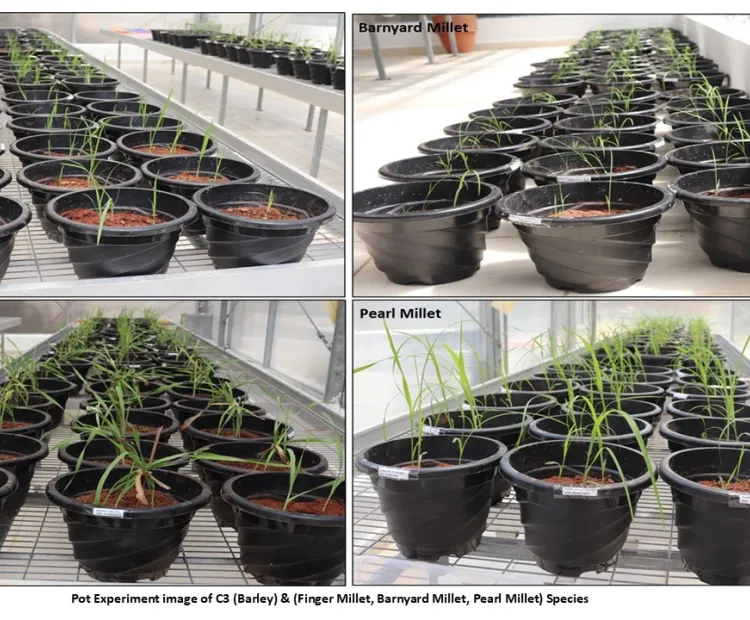
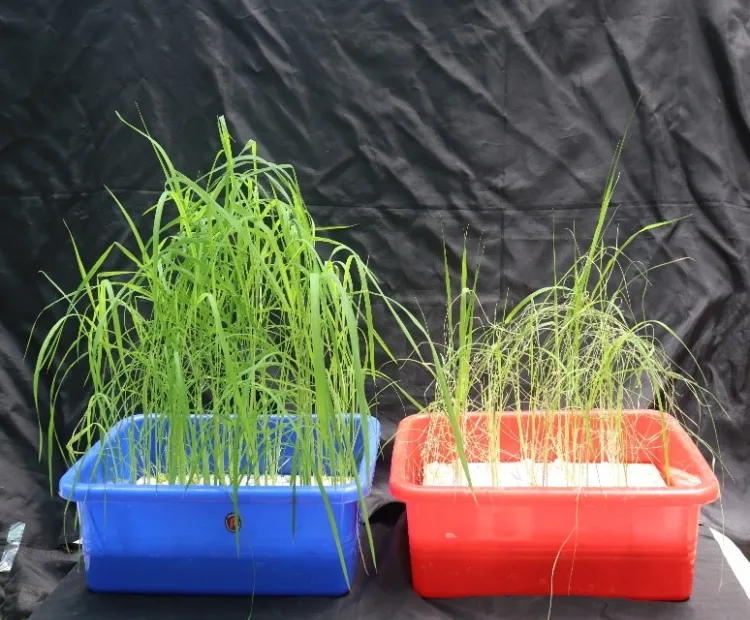
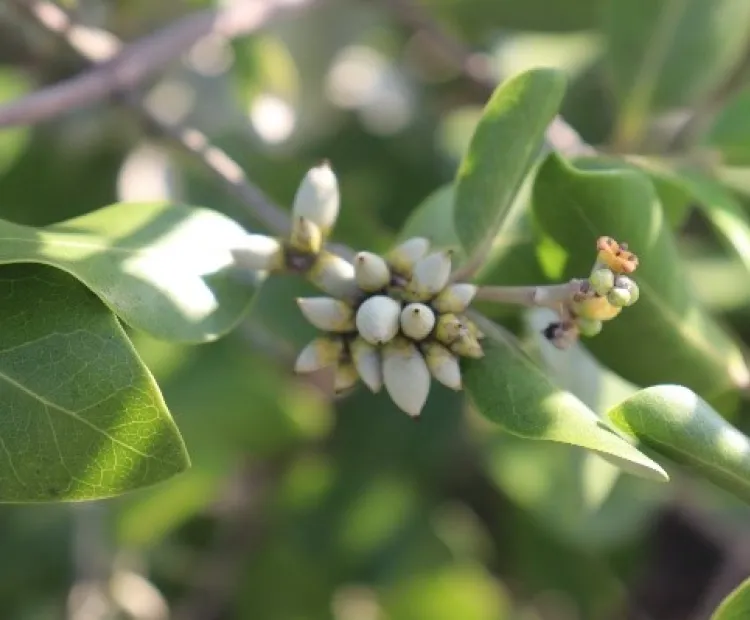
Funded – DeFries Bajpai Foundation
Duration- 4 months (April, 2027)
Location - Microbiology Lab
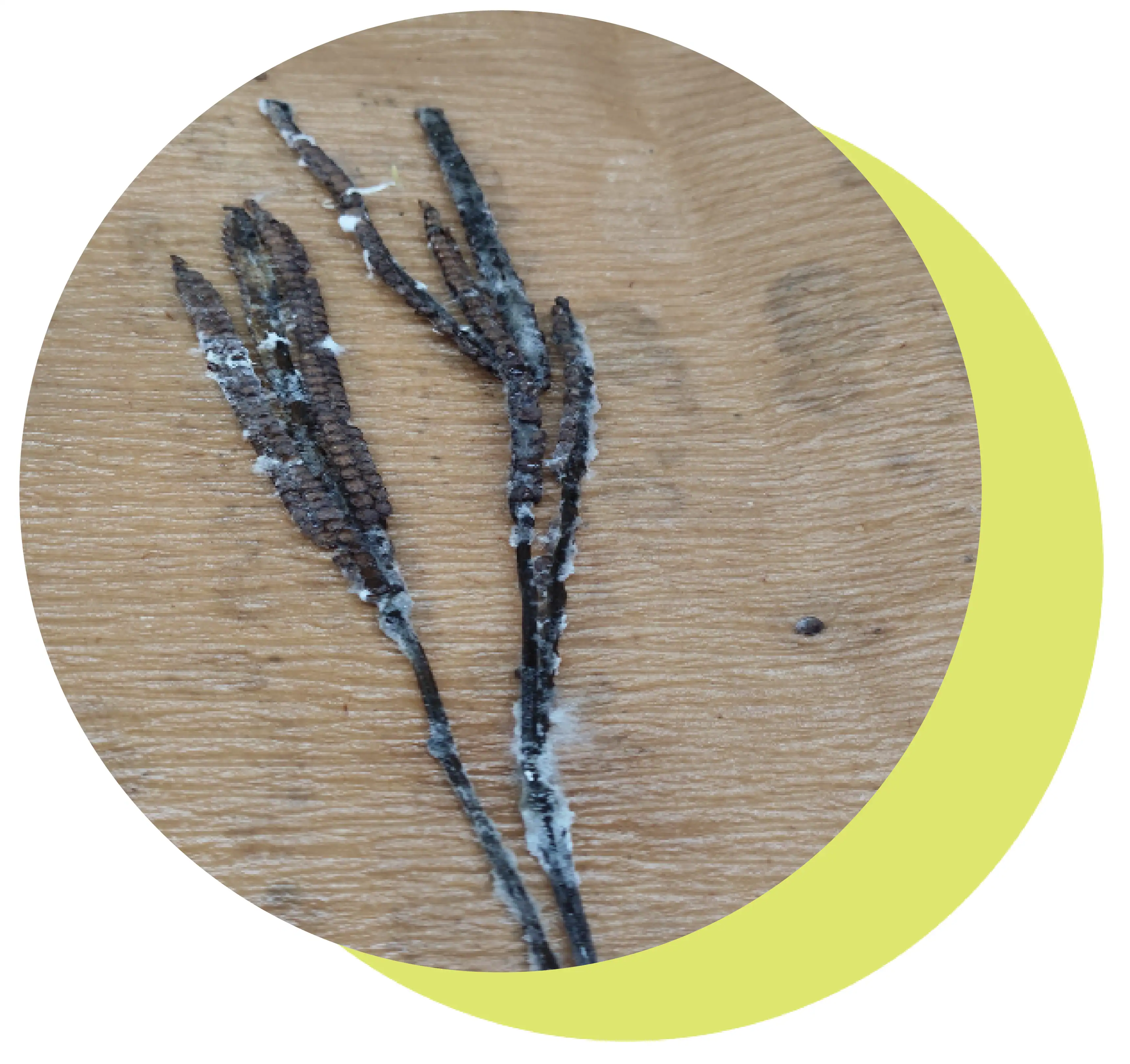
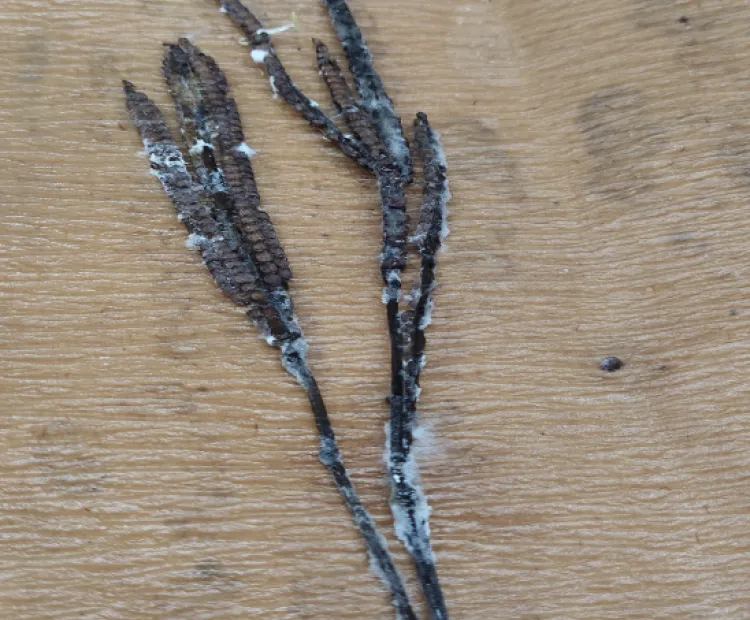
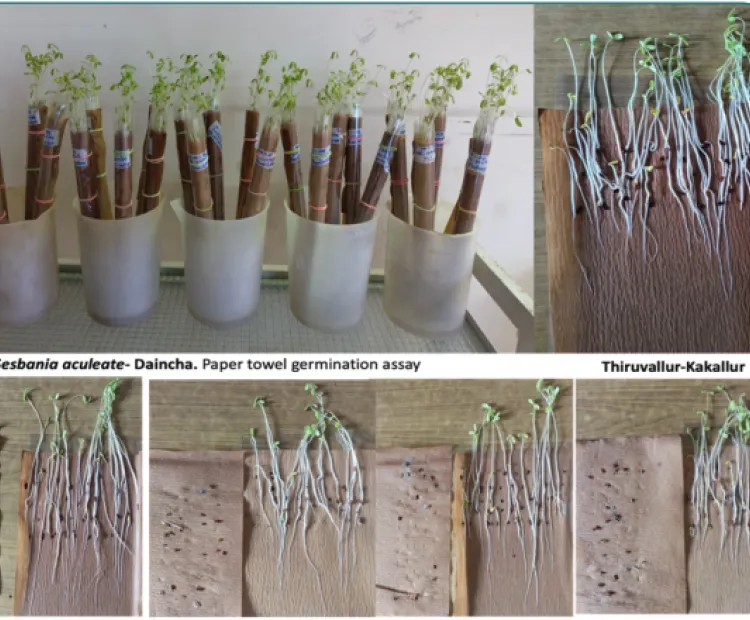
Kodo millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum L.) is a climate-resilient, nutrient-rich grain with growing appeal as a functional food. However, its consumption poses a health risk due to fungal contamination, particularly by Aspergillus species producing cyclopiazonic acid (CPA), a potent mycotoxin. This study investigates the prevalence of Kodo millet poisoning in Tamil Nadu, examining cultivation and post-harvest practices that contribute to contamination. Despite its many advantages Kodo millet faces a major challenge, due to fungal contamination. such as Aspergillus tamarii and Aspergillus flavus, which produce cyclopiazonic acid (CPA), a neurotoxin and hepatotoxin. Consumption of contaminated millet can lead to severe poisoning, causing symptoms such as vomiting, tremors, giddiness, difficulty in swallowing and in extreme cases death. The study explores the diversity of the fungal pathogen responsible for the aflatoxin contamination and determine the aflatoxin.
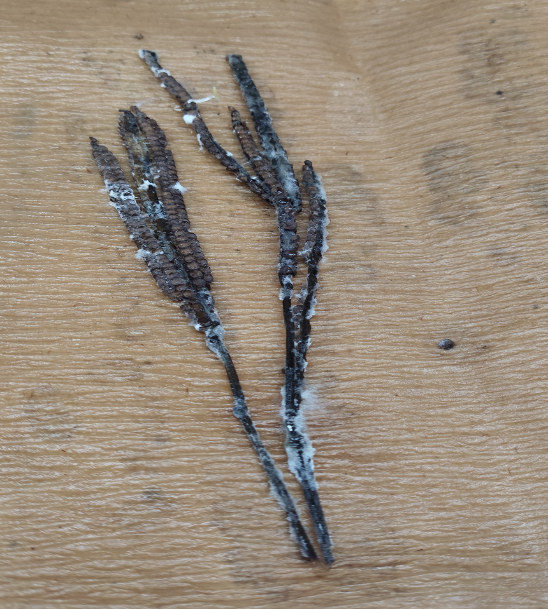

a. Contaminated panicle
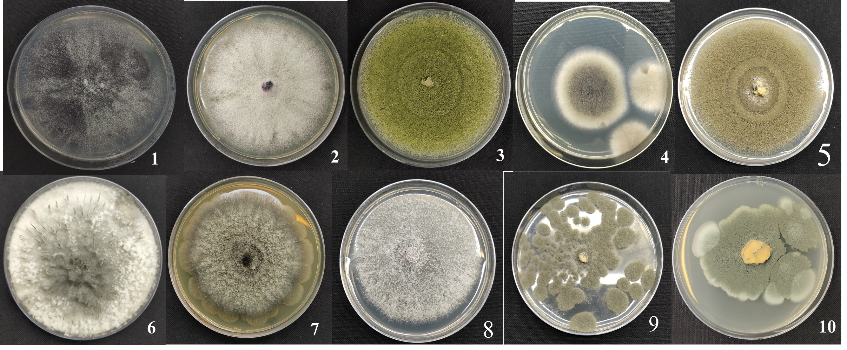
b. Isolation of fungal pathogens